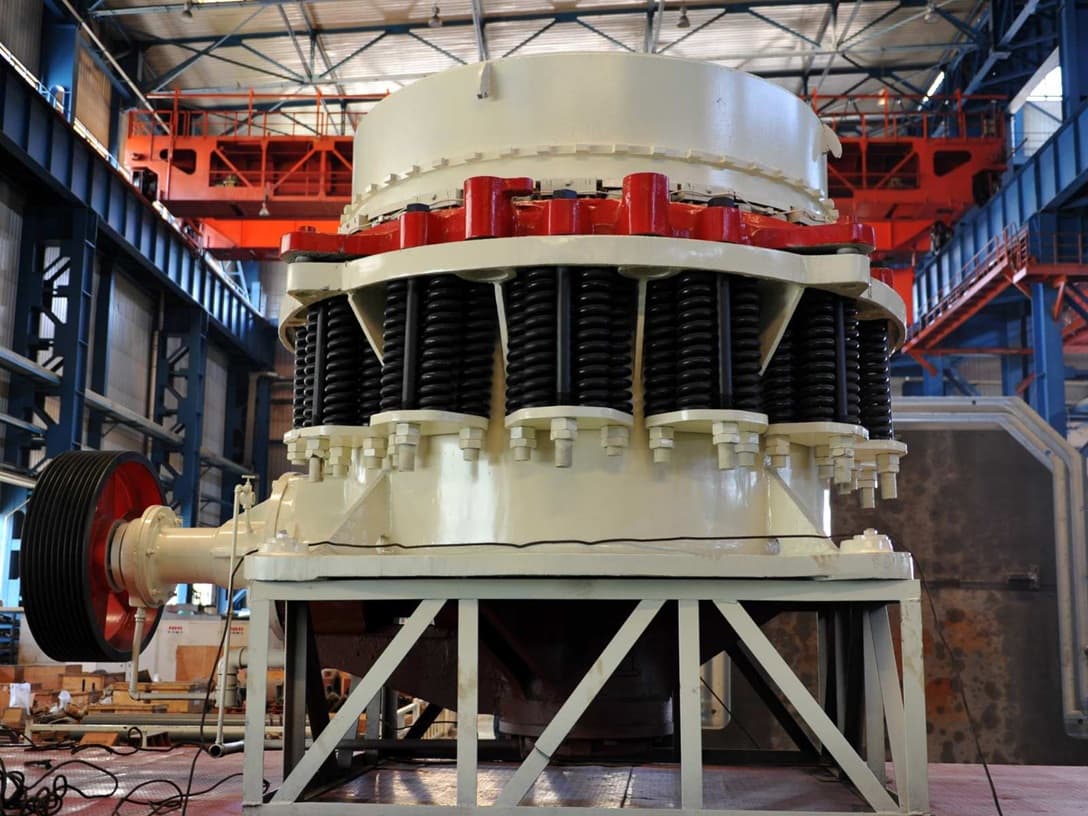
Imagine you are in charge of a busy construction site. You need rock crusher cones to crush hard stone into smaller pieces. These machines help you work faster and make your job easier. If you know how high-efficiency industrial cone crusher technology works, you can save up to 15% on energy bills. You can also lower maintenance costs by almost one third. This knowledge helps your site run well and saves money every day.
What Are Rock Crusher Cones
Definition
Rock crusher cones break hard rocks into smaller pieces. They squeeze stones between a moving cone and a bowl. The cone spins inside the chamber. This crushes the rocks until they are small enough. These machines are compression crushers. The mantle turns inside a bowl lined with manganese. You get smaller rocks and even results every time.
Tip: Rock crusher cones work best for medium or hard rocks.
-
Rock crusher cones crush medium and hard mineral rocks.
-
They use less energy and work faster than other crushers.
-
You can quickly turn big rocks into small ones.
Key Features
Rock crusher cones have a special design. Each part helps crush rocks and makes the machine last longer. Here is a table that shows the main parts and what they do:
|
Component
|
Location
|
Purpose
|
Function
|
|
Crushing Chamber
|
Middle of the crusher
|
Holds the crushing process
|
Has the bowl liner and mantle; controls how rocks get smaller
|
|
Mantle
|
Inside the chamber
|
Crushes the rocks
|
Made of strong materials; moves in circles to press rocks
|
|
Concave (Bowl Liner)
|
Around the mantle
|
Outer cone that stays still
|
Tough surface for the mantle to press rocks against
|
|
Eccentric Assembly
|
Next to the main shaft
|
Makes the cone move in circles
|
Turns to help the mantle move around
|
|
Adjustment Ring
|
On the bowl assembly
|
Changes the size of output
|
Raises or lowers the bowl to make rocks bigger or smaller
|
Modern rock crusher cones have new features to help them work better:
|
Performance Feature
|
Description
|
|
High Reduction Ratio
|
Makes big rocks into small ones quickly
|
|
Energy Efficiency
|
Uses less power for the same job
|
|
Durability
|
Handles tough rocks and needs less fixing
|
|
Automation
|
Lets you change settings fast for better results
|
|
Advanced Materials
|
Uses strong parts so you fix it less often
|
Advantages
Rock crusher cones give you many good things at your site. Here are the main benefits:
-
You get even, high-quality rocks. The pieces are all the same size, which helps with building roads and buildings.
-
You save energy. These machines use compression, so you spend less on power and fuel.
-
The machine lasts longer. The parts wear out slowly, so you do not need to fix or replace them often.
Rock crusher cones help you work faster and better. You can use them in quarries, mines, and recycling centers. These machines give you exact results and keep your work going smoothly. You can change the settings easily and get the right size rocks for your job.
Cone Crushers: How They Work
Components
You find several important parts inside cone crushers. Each part helps you get the best results from your crushing tasks. The mainframe gives strong support and keeps everything steady. The crushing chamber lets rocks move smoothly and helps you get even sizes. The mantle and concave do most of the crushing work. These parts use tough materials to handle hard rocks. Bearings help the machine run smoothly and carry heavy loads. You need to check these parts often to keep your cone crushers working well.
|
Component
|
Function
|
|
Mainframe
|
Gives support and keeps the machine stable during crushing.
|
|
Crushing Chamber
|
Helps rocks move and ensures even product size.
|
|
Mantle and Concave
|
Crush rocks and decide how fine the final product will be.
|
|
Bearings
|
Reduce friction and help the machine run smoothly.
|
Tip: Regular checks on bearings and the crushing chamber help you avoid costly repairs.
Crushing Process
Cone crushers use a special crushing process. You feed rocks into the top. The mantle moves in a circle inside the crushing chamber. Rocks get squeezed between the mantle and the concave. This action breaks the rocks into smaller pieces. You can choose different crushing chambers for different jobs. Each chamber changes the feed size, discharge size, and crushing ratio.
|
Crushing Chamber Type
|
Feed Size (mm)
|
Discharge Size (mm)
|
Crushing Ratio
|
Production Capacity
|
|
Standard Crushing Chamber
|
100-350
|
35-65
|
4-6
|
High
|
|
Medium Crushing Chamber
|
50-150
|
10-35
|
6-8
|
Moderate
|
|
Short-Head Chamber
|
25-50
|
3-10
|
8-10
|
Low
|
You get to pick the right chamber for your crushing needs. This choice helps you control the size and quality of your final product.
Types
You can use different types of cone crushers for different crushing jobs. Each type fits a special role in mining, quarrying, or recycling.
|
Type of Crusher
|
Description
|
Typical Applications
|
|
Secondary Crushers
|
Take big rocks from primary crushers and make them smaller.
|
Mining, quarrying for aggregate production
|
|
Tertiary Crushers
|
Make rocks even smaller for final use.
|
Final product prep in mining
|
|
Fine Crushers
|
Also called sand crushers, make very fine material.
|
Recycling, making fine aggregates
|
-
Mining: You use cone crushers for crushing hard materials.
-
Quarrying: Cone crushers help you make lots of aggregates.
-
Recycling: You use cone crushers to crush asphalt and other materials.
You can see how cone crushers give you many choices for your crushing needs. You get the right size and shape for every job.
Technology in Cone Crushers
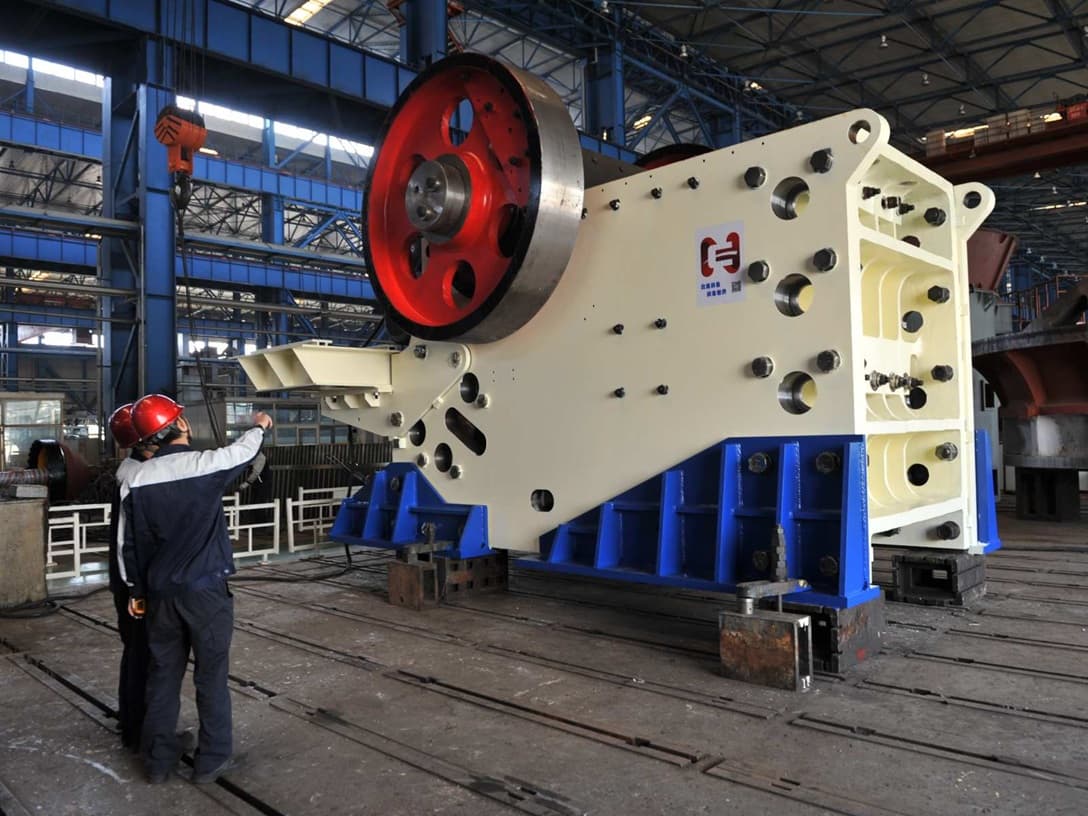

Design Innovations
Modern cone crushers have many new features. These changes help you work faster and stay safe. The HP350e model works up to 10% better than old models for secondary jobs. You can pick different settings to fit your needs. No-backing liners let you change parts quickly and keep things clean. A feed cone lifting tool helps you move the feed cone safely. Tramp release cylinders make fixing the machine easier. The head anti-spin brake helps the liner last longer. You can get chambers made for special jobs, so you always get good results. Many parts also fit older HP300 models, so you save money when you upgrade.
|
Innovation
|
Description
|
|
Enhanced Performance
|
HP350e boosts output by up to 10% in secondary applications.
|
|
Kinematics Options
|
Pick settings for high capacity or lower throughput.
|
|
No-Backing Liners
|
Change liners quickly and safely.
|
|
Feed Cone Lifting Tool
|
Move the feed cone without risk.
|
|
Tramp Release Cylinders
|
Make service and maintenance easier.
|
|
Head Anti-Spin Brake
|
Protect liners and extend their life.
|
|
Application-Specific Chambers
|
Get the right chamber for each crushing job.
|
|
Aftermarket Support
|
Use parts from older HP300 cones to save costs.
|
Automation
Automation makes cone crushers smarter and safer. You do not have to change settings by hand. The system checks the load and changes settings for you. This keeps your cone crusher working well. You get alerts if something is wrong. You can fix problems before they get worse.
“Automation ensures the best possible performance,” said Vincent Celsi, vice president of crushers for Metso Outotec. In Metso’s MX cone crusher line, settings are automatically adjusted based on load conditions, which improves the utilization of wear parts as well as worker safety.
-
Automation systems keep you away from danger.
-
Real-time monitoring warns you about unsafe things.
-
You can fix problems before the machine fails.
-
Automated alerts help you spot issues like bowl float and stop damage.
Safety
Safety features keep you and your team safe when using a heavy duty hydraulic cone crusher. Hydraulic chamber clearing opens the crusher to a safe spot. Hydraulic overload relief stops damage from heavy loads. Hydraulic adjustment lets you change settings without touching moving parts. Common Level Design means you do not need much maintenance. Centralized control lets you stop everything from one place. Conveyor safety features help keep your site safe. Hydraulic overload protection and automated controls make your work safer every day.
-
Hydraulic chamber clearing system opens the cone safely.
-
Hydraulic overload relief protects parts from damage.
-
Hydraulic adjustment keeps output steady.
-
Centralized control allows emergency stops.
-
Conveyor safety features reduce risks.
-
Automated systems improve safety for everyone.
Applications
Mining
Cone crushers are used a lot in mining. They break big rocks into smaller pieces. This step is needed before getting minerals out. Cone crushers work well with hard and rough stone. They crush ores like iron, copper, and gold. You need these machines to get raw material ready for the next step. Using crushers in mining helps you save time and get better results.
Construction
You see cone crushers on large building sites. They make raw materials smaller and easier to use. This is the first step to make aggregates for roads and buildings. Crushing equipment helps you meet size and quality rules. You can trust crushers to give you the right material for concrete and asphalt. Using crushers in construction keeps your project on time and on budget.
Tip: Cone crushers help you get the right size of aggregate for any job.
Recycling
Cone crushers can recycle concrete, bricks, and asphalt. These machines turn waste into new building material. You help the planet by using less landfill space. Crushers break down old roads and buildings so you can use the material again. Here is how crushers help in recycling:
|
Role of Cone Crushers in Recycling
|
Description
|
|
Construction Waste Recycling
|
Turns concrete, bricks, and asphalt into new aggregates, so you use landfills less.
|
-
Crushers are used for fine crushing of asphalt.
-
The machine squeezes the material to shape it.
-
You get good recycled asphalt that fits your needs.
Other Industries
Cone crushers are used in many other jobs. They help you process sand, gravel, and building materials. You also use them in mineral plants. Here is where you might use crushers:
|
Industry
|
Material Processed
|
|
Construction
|
Concrete, asphalt, and aggregate used again on job sites
|
|
Mining
|
Big stones made smaller for more processing and extraction
|
|
Recycling
|
Old building parts turned into new material
|
You can trust crushers to do hard work in any industry. They help you get raw materials ready for many uses and always work well.
Cone Crusher Maintenance
Daily Tasks
You should check your crusher every day. These checks help you find problems early. This way, you can avoid big repairs. Start by looking at the machine for leaks or broken parts. Check for any trash or dirt around the crusher. Make sure the oil is clean and at the right level. Look at the hydraulic system pressure. It should match what the maker says. Write down the temperatures while the crusher runs. If the oil or bearings get too hot, there could be a problem. Listen for odd sounds like grinding or knocking. These noises can mean something is wearing out.
Here is a table to help you remember your daily tasks:
|
Daily Maintenance Task
|
Description
|
|
Visual inspection of the crusher
|
Check for oil leaks, worn parts, or debris buildup around the machine.
|
|
Lubrication system check
|
Make sure oil levels are correct and clean.
|
|
Check hydraulic system pressure
|
Confirm settings match manufacturer recommendations.
|
|
Monitor and log operating temperatures
|
Watch for spikes in bearing or oil temperature.
|
|
Listen for unusual sounds
|
Grinding or knocking can mean component wear or failure.
|
Check if all moving parts have enough oil. Make sure the rocks you put in are the right kind. Using the wrong rocks can wear out the crusher faster. Look for leaks in the hydraulic system. Leaks can be dangerous.
Tip: Daily checks help you find problems early. Use a checklist to keep track and train your team to follow it every day.
Weekly Checks
Weekly checks go further than daily ones. Look for wear on the mantle and concave. Check if all bolts are tight. Loose bolts can break the machine. Look at the belts and pulleys for cracks or damage. Clean off dust and dirt from the crusher. Make sure the oil and filters are not dirty. If the oil is dirty, change it right away. Listen to the bearings for strange sounds or heat. These steps help your crusher last longer.
-
Look for wear on important parts.
-
Tighten all bolts.
-
Clean dust and dirt from the crusher.
-
Check belts and pulleys for damage.
-
Change oil and filters if they are dirty.
-
Listen for odd sounds from bearings.
Doing these checks each week helps you catch small problems. This keeps your crusher working well for a long time.
Long-Term Care
Long-term care helps your crusher last for years. You need to do preventative maintenance. Take care of the bearings so they last longer. Change the oil often. Clean the bearings to keep out dust and dirt. Watch the bearing temperatures. If they get too hot, stop and fix the problem. Check the seals to stop oil leaks.
Follow these steps for long-term care:
-
Take care of bearings so they last longer.
-
Change oil when needed.
-
Clean bearings to keep out dirt.
-
Watch bearing temperatures and stop if too hot.
-
Check seals to stop leaks.
Good maintenance can make your crusher parts last 30% longer. This saves you money and keeps your machine working well.
Common Mistakes
Many people make the same mistakes when caring for crushers. These mistakes can break the machine and stop work. Here is a table of common mistakes and what can happen:
|
Maintenance Mistake
|
Consequence
|
|
High Oil Temperature
|
Can lead to equipment failure if not fixed.
|
|
Oil Temperature and Pressure Rise
|
May mean clogging or faulty parts. Needs quick attention.
|
|
Low Oil Pressure After Oil Pump Startup
|
Can cause poor lubrication and severe damage.
|
|
Oil Containing Fine Mud and Impurities
|
Leads to early wear and failure of parts.
|
|
Presence of Water in the Oil
|
Causes rust and corrosion, leading to big problems.
|
|
Excessive Vibration of the Cone Crusher
|
Shows mechanical issues that can cause more damage.
|
You need to watch for these mistakes. Fix them fast to stop bigger problems. Always use clean oil and check for leaks. Never ignore strange sounds or shaking.
Tools
You need the right tools to take care of your crusher. Lifting tools help you move heavy parts safely. Special tools let you change worn parts quickly. An advanced mounting rack makes changing parts easier and faster.
|
Tool Type
|
Description
|
|
Lifting tools
|
Help you move heavy parts safely and keep your team safe.
|
|
Specialist tooling
|
Lets you change wear parts quickly and safely.
|
|
Advanced Concave mounting rack
|
Makes changing wear parts easier and reduces downtime.
|
Note: Using the right tools keeps your team safe and helps you finish maintenance faster.
Keep these tools ready at all times. They help you do maintenance with less risk and more speed.
Troubleshooting
Common Issues
Sometimes, cone crushers have problems. These problems can slow your work or break the machine. Here are some issues you might see:
-
Oil gets too hot if oil is bad or too low.
-
Oil temperature and pressure go up if tubes are blocked.
-
Oil pressure is low after starting if pipes are blocked.
-
Oil gets dirty with mud if seals do not work.
-
Water gets in oil from leaks or pressure trouble.
-
The crusher shakes a lot if the base is loose or rocks are too hard.
-
The crushing cone spins too fast if there are oil issues.
-
The moving cone speeds up fast if bearings are broken.
-
The shaft does not spin evenly if gears are damaged.
-
You hear splitting sounds if lining plates are loose.
-
The coupling spins but the crusher does not move if keys are broken.
-
Loud knocking happens if gears are not put in right.
-
The supporting ring jumps if something gets stuck inside.
-
Big pieces come out if liners are worn out.
Tip: Check your crusher often. Finding problems early keeps your site safe and stops bigger trouble.
Solutions
You can fix most cone crusher problems with easy steps. The table below shows what to do for each problem:
|
Problem Description
|
Recommended Action
|
|
Oil containing fine mud and impurities
|
Turn off the machine, seal or clean the dustproof part, and change the dirty oil.
|
|
Low oil pressure after oil pump startup
|
Warm up the oil, fix or change the oil pump, and clear or change blocked pipes.
|
|
Splitting sounds during operation
|
Stop the crusher, tighten screws, and check for a fallen zinc layer.
|
|
Presence of water in the oil
|
Clean the oil tank, change the oil, fix or change the cooler, and clean the return pipe.
|
|
Excessive vibration of the cone crusher
|
Tighten bolts, control what you feed, change broken parts, and make sure there is enough oil.
|
|
Non-uniform rotation of the transmission shaft
|
Change gears, make sure they fit right, and change connection keys.
|
|
High rotation speed of the crushing cone
|
Fix or change bushings and spindles, add oil, and adjust bushing space.
|
|
Sudden acceleration of the moving cone
|
Adjust the gap to fix the problem.
|
|
Coupling rotation without crusher movement
|
Take apart the machine to find and change broken parts.
|
|
Strong knocking in the drive shaft
|
Fix how gears fit together or change the gear.
|
|
Increased size of material output
|
Check if the liner is worn, change the outlet size, and change the lining plate if needed.
|
|
Supporting ring bounces
|
Screen better to keep out big things and think about adding an iron remover.
|
Most problems can be fixed by doing these steps. Checking your crusher often and fixing things fast helps it last longer and work better.
Rock crusher cones help you get good results in mining, construction, and recycling. You can save money if you follow a regular maintenance plan. Daily checks stop breakdowns and help your equipment last longer. Watch oil temperature and pressure to keep things running well. Always fill the crushing chamber to get the best results. Learning about new technology gives you more control and less waiting for repairs.
|
Feature
|
Benefit
|
|
Adjustable Output Size
|
Makes your product better
|
|
Automation
|
Fewer manual checks needed
|
Keep learning and ask experts for help to keep your work going strong.

 USTEU’s Guide to Smarter, Safer Home Charging
USTEU’s Guide to Smarter, Safer Home Charging